How to Protect Trade Marks in China?
To protect your trademark in China in an economical way, registering it with the China Trademark Office (CTMO) should be taken into consideration.Under China’s laws and regulations on the basis of unfair competition, without a registration, enforcement is still technically possible, but generally protection under such laws is much less predictable and normally more expensive.
“First-to-file” Principle
China adopts “first-to-file” principle for obtaining trademark rights. This means that generally the person who files their trademark application first can register the trade mark. It is therefore highly advisable to file applications for trademarks as early as possible, and preferably well before you enter the Chinese market.
Chinese Character Trade Marks
Chinese consumers prefer the Chinese versions of the brand, because Chinese is their mother tongue. So if you don’t have a Chinese name for your English mark, you are strongly advised to create one and register it. If not, the local market will voluntarily create one for you (which you might not like) and the third party might register it.
Guidance to Register the Trademark
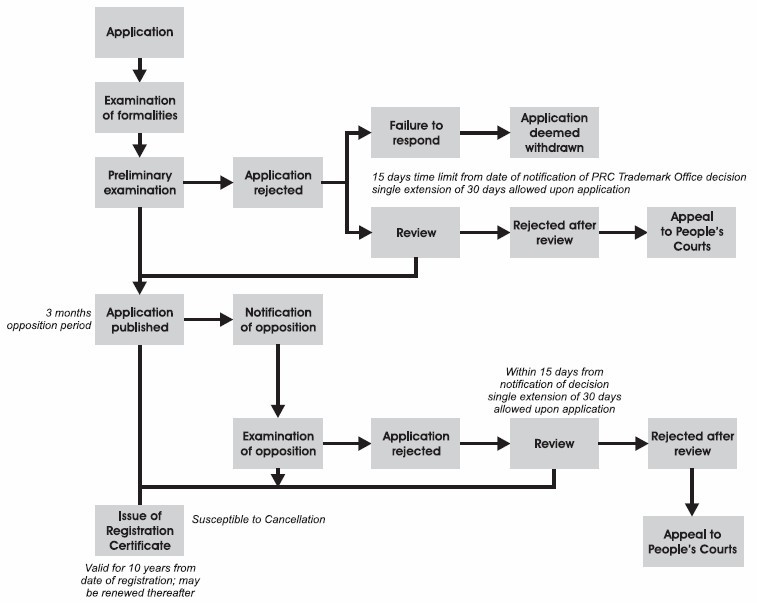
- There are two ways to file the application: filing an application directly with the China Trademark Office or alternatively by extending an existing application or registration to China under the Madrid Protocol.
- If you choose to file the application directly, you must file through a local Chinese trademark agency.
- It is generally preferable in China to file for the version of a mark as it is used and to cover as wide a range of goods and/or services as you reasonably can.
- Before filing your trademark, trademark searches are advised to conduct to check whether anyone else has already filed for a similar or identical mark which might block your planned application.
- Once approved, the application will be published in the CTMO Gazette. During the following three months after the publication, any party may file an opposition against your mark, challenging the application on the grounds of prior marks, distinctiveness or other grounds set out in the Trademark Law. A registration certificate will be issued if no opposition is filed within this three-month period.
- The validity period of a registered Chinese trademark is 10 years and can be renewed every 10 years.
- Normally, it takes 18 months to obtain a trademark registration in China, with protection generally effective on the date of registration.
To prevent someone else registering a trademark similar or identical to your mark in China, what can you do?
The best way to prevent this type of “counterfeiting” is registering your marks early. But if someone already files your trade mark, an opposition can be submitted once it is published in the Trademark Gazette. An opposition will normally take 18 months. The loser in an opposition can file an appeal to the TRAB which will normally take a further 18 months to issue a decision. The decisions of the TRAB can be appealed further to the Intermediate People’s Court in Beijing.
What if someone else has already registered my trademark in China?
Trademarks registered by others can be canceled through the filing of petitions with the TRAB. It is normally advisable to support such cancellation actions through extensive evidence of the fame and use of your mark, both in China and globally.
But if someone has registered your mark and has not used it for three years, it is possible to petition the CTMO to cancel the registration on the grounds of non-use for three years.
Outline of the Trade Mark Application / Opposition / Appeal Process